Understanding AC to DC Converters: Powering Our Modern World
In today’s fast-paced technological world, AC to DC converters play a crucial role in powering everything from small household gadgets to massive industrial machinery. This article explores the importance of these converters, their working principles, and their applications across various sectors. By the end of this read, you’ll understand why AC to DC converters are indispensable and how they make our electronic world possible.
Table of Contents
Outline
- What is an AC to DC Converter?
- Why is AC Power Converted to DC?
- Key Components of AC to DC Converters
- How Does an AC to DC Converter Work?
- Types of AC to DC Converters
- Applications of AC to DC Converters
- The Role of Transformers in Power Conversion
- Understanding Voltage and its Importance
- Common Challenges in AC to DC Conversion
- Future Trends in Power Conversion Technology
What is an AC to DC Converter?
An AC to DC converter is a device that converts alternating current (AC), which changes direction periodically, into direct current (DC), which flows in a constant direction. This conversion is essential because most electronic devices, including computers and smartphones, operate on DC power.
Why is AC Power Converted to DC?
AC power is widely used for transmitting electricity because it can easily travel over long distances. However, most electronic devices require DC power for operation. Hence, converting AC to DC is crucial for the functionality of our everyday gadgets. This process ensures that devices receive the stable DC voltage they need to function correctly.
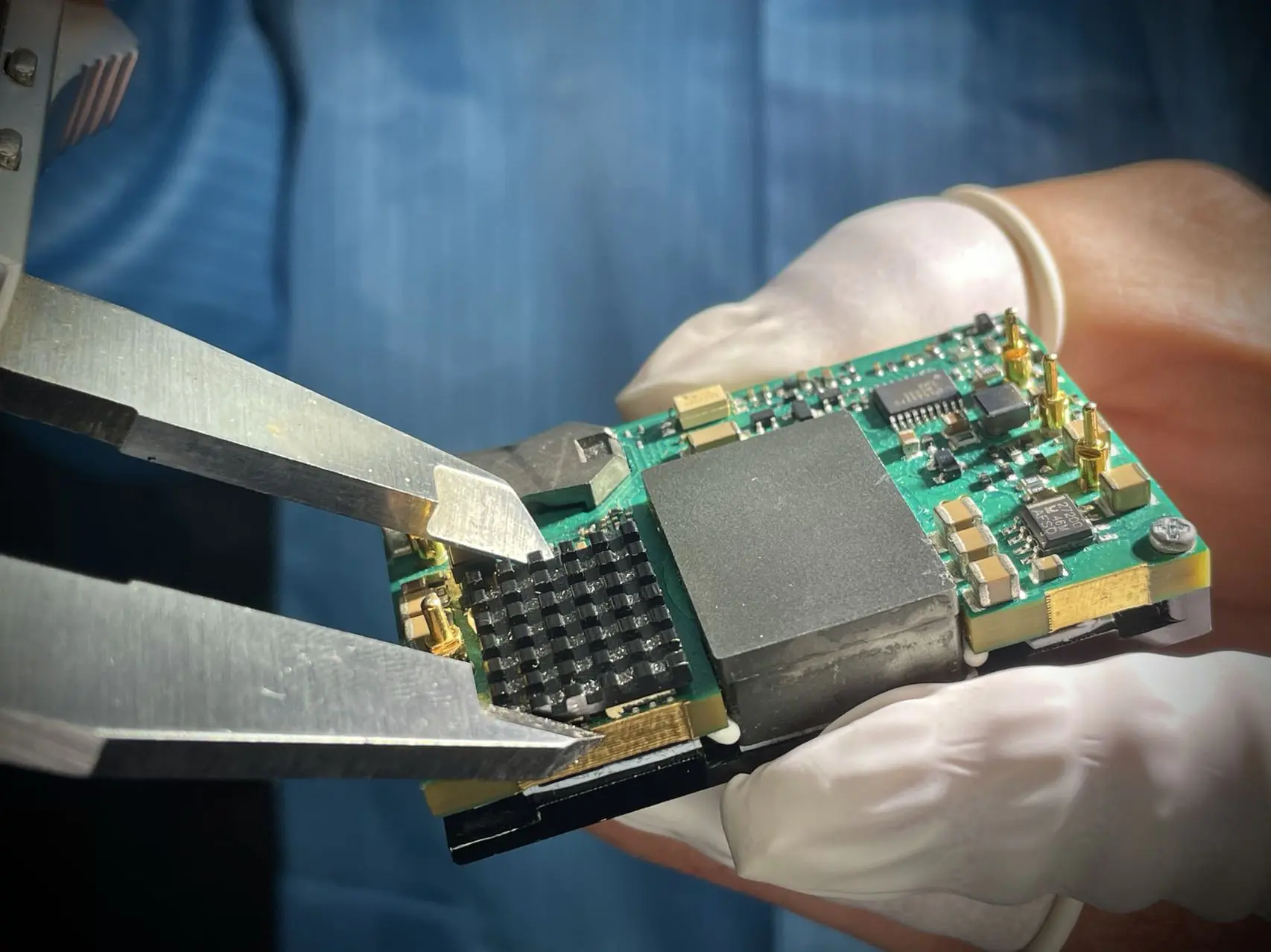
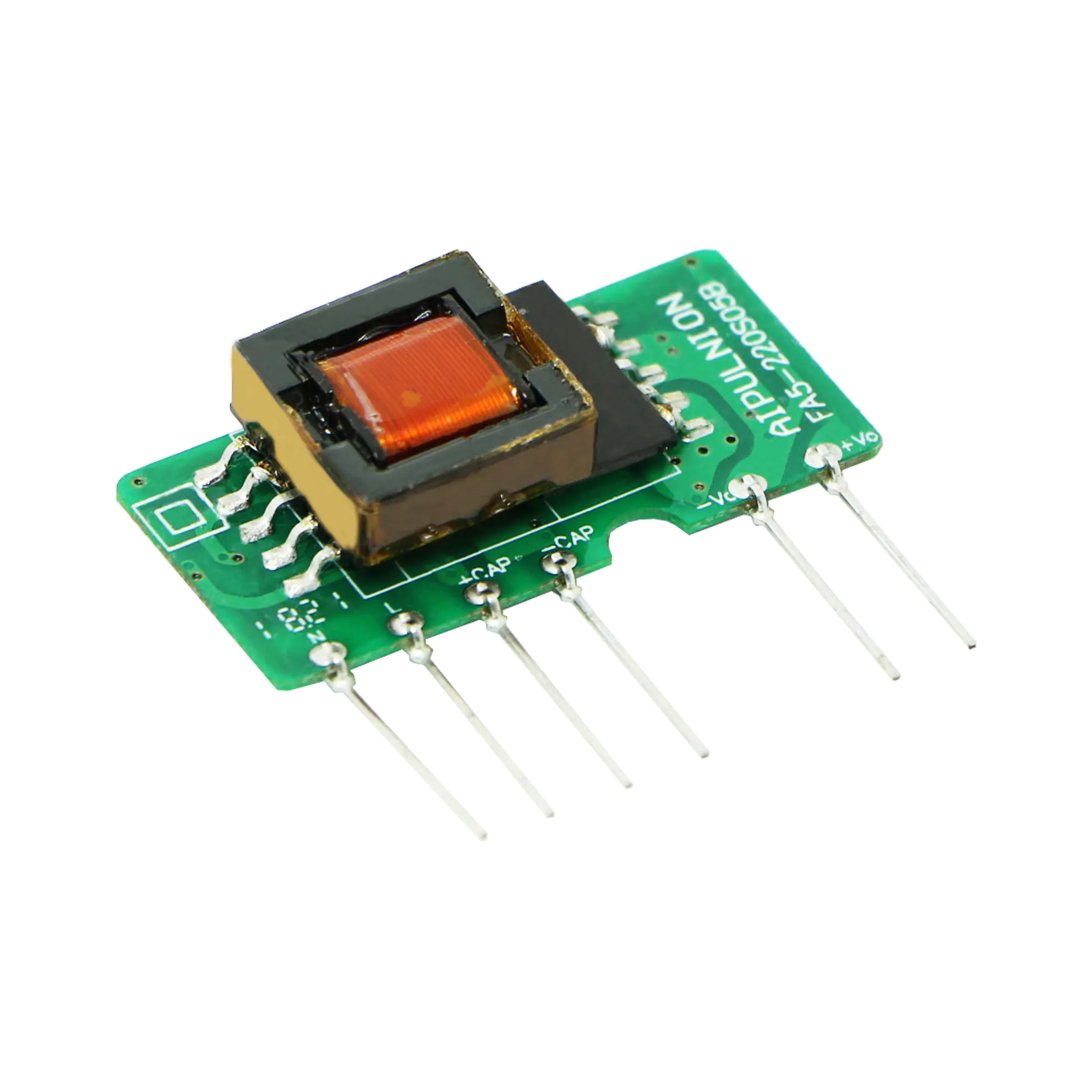
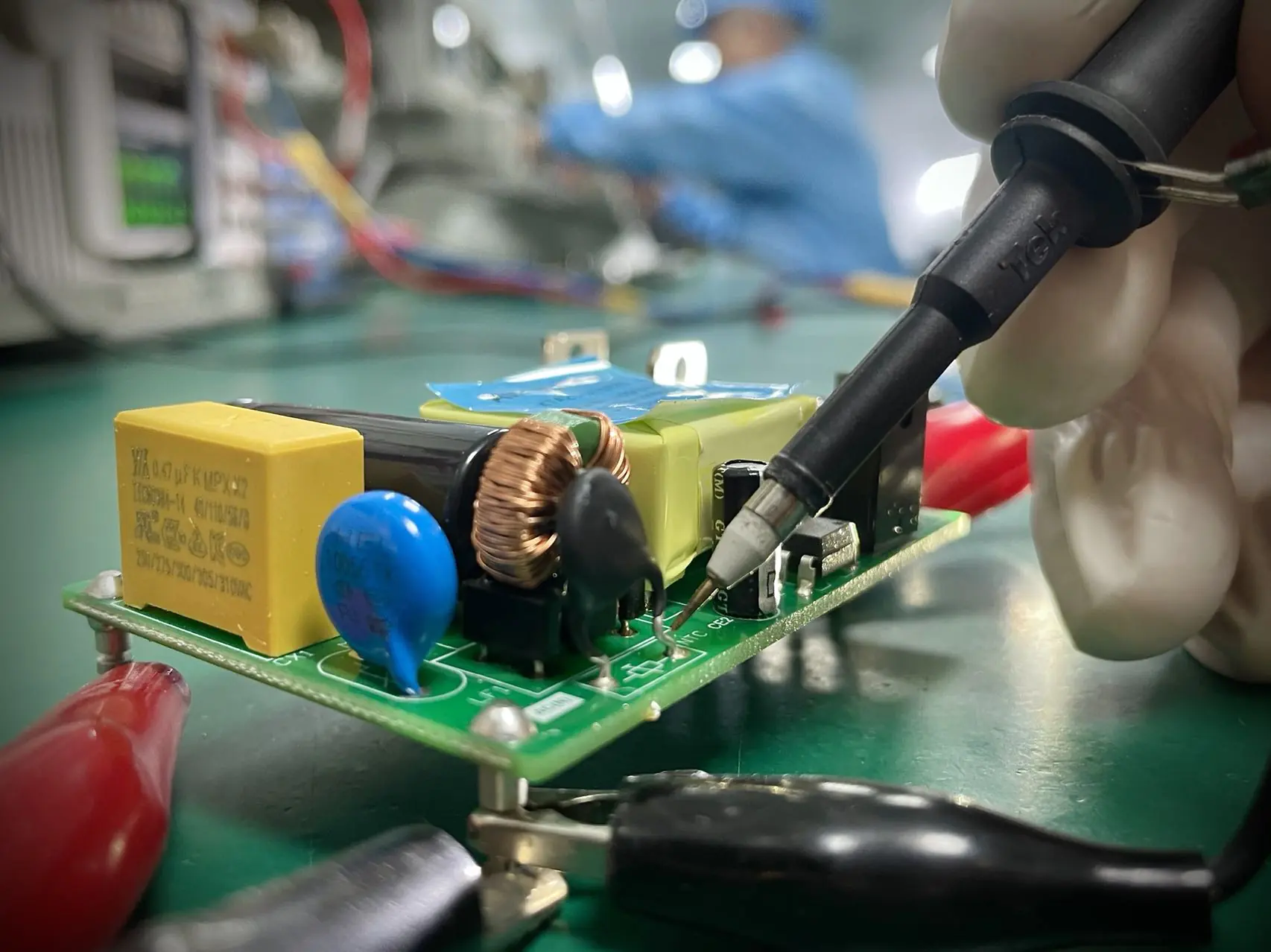
Key Components of AC to DC Converters
The main components of an AC to DC converter include:
- Rectifier: Converts AC to DC.
- Transformer: Adjusts the voltage level.
- Capacitor: Smoothens the DC output.
- Regulator: Maintains a constant output voltage.
These components work together to ensure efficient power conversion.
How Does an AC to DC Converter Work?
The conversion process begins with the rectifier circuit, which uses diodes to allow current to flow in only one direction, effectively converting AC to DC. The capacitor then smoothens this pulsating DC into a more stable DC voltage. Finally, the regulator ensures that the output voltage remains constant, even if the input voltage or load conditions change.
Types of AC to DC Converters
AC to DC converters come in various forms, each suited to different applications:
- Linear Converters: Known for their simplicity and low noise, used in low-power applications.
- Switching Converters: More efficient and suitable for high-power applications, such as in industrial power supplies.
Each type has its advantages, depending on the specific requirements of the application.
Applications of AC to DC Converters
These converters are vital in numerous applications:
- Consumer Electronics: From charging devices to powering home appliances.
- Industrial Applications: Used in machinery and control systems.
- Renewable Energy Systems: Convert AC generated by wind turbines or solar panels to DC for storage or further use.
The versatility of these converters makes them integral to modern technology.
The Role of Transformers in Power Conversion
Transformers play a crucial role in adjusting the input voltage to the desired level before conversion. By using a transformer, converters can handle high ac voltage levels safely, reducing them to manageable levels for conversion to DC.
Understanding Voltage and its Importance
Voltage is a measure of electrical potential difference. In power conversion, maintaining the correct voltage is crucial to ensure the safe and efficient operation of electronic devices. Output voltage stability is a primary concern in designing AC to DC converters.
Common Challenges in AC to DC Conversion
Some challenges include:
- Heat Dissipation: Managing excess heat generated during conversion.
- Efficiency: Ensuring minimal energy loss during the conversion process.
- Electromagnetic Interference: Minimizing noise that can affect other electronic components.
Addressing these challenges is key to developing reliable converters.
Future Trends in Power Conversion Technology
The future of power electronics lies in creating more efficient power converters with higher power density and lower environmental impact. Innovations like semiconductor materials and improved circuit designs are paving the way for advanced converters that can handle more power with less energy loss.